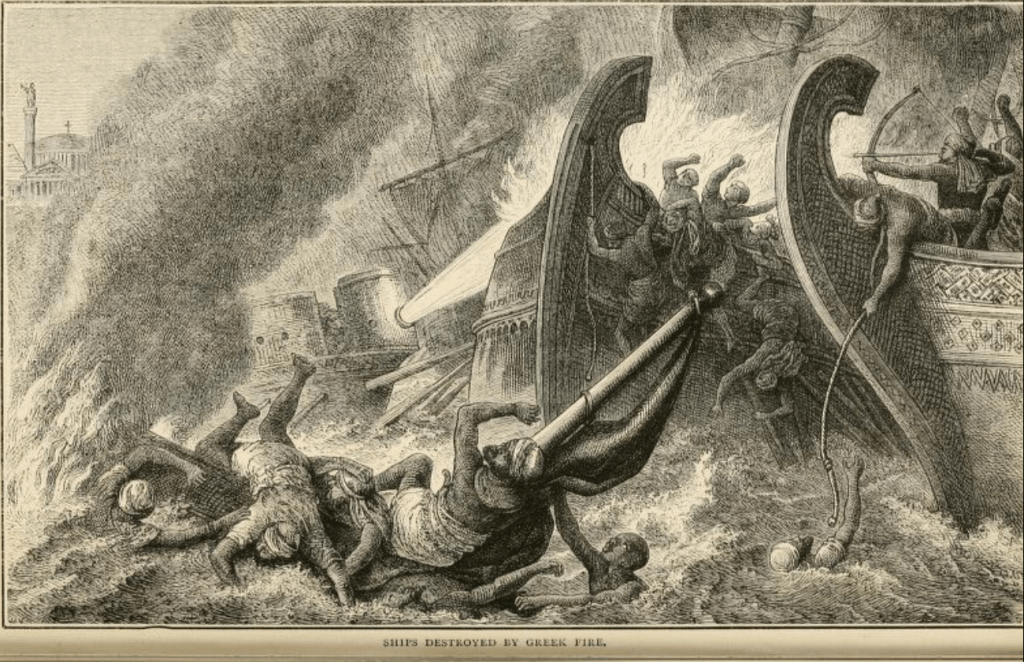
September 1, 718. With the clear motivation to defend Constantinople, Byzantine ships filled with anxious soldiers were surrounding the mainland. On the horizon, Arab Muslim forces, bringing with them a fleet of large and robust wooden ships, started to form a blockade. Slowly but surely, they advanced towards each other. Once the two mighty forces collided with each other, both sides swung their swords and flung their arrows. Not long after the battle began, the Byzantines ordered their reserved ship to sail to the front line. This ship carried something that would be the most destructive form of weaponry the world had even seen up to that point. Once the ship got close to the Arab fleet, the Byzantine soldiers scuttled around and turned on a nozzle fueled with Greek fire.
In the many years leading up to this battle, the Byzantine Empire, previously known as the eastern portion of the Roman Empire, and the Arab nations, united under the banner of Islam, had been engaged in constant warfare. This conflict was known as the Arab-Byzantine Wars, which lasted from 629 to 1050 CE. The rulers (also known as caliphs) of the Islamic Empire sought to expand outwards to spread the religion of Islam, and did so by invading northern Africa. From there, they took control of the Iberian Peninsula, threatening to overrun Western Europe. The Islamic Empire also desired to take control of Eastern Europe, which, of course, became problematic to the Byzantine Empire that dominated the northeastern Mediterranean. As a result, the Islamic Empire attempted to claim the wealthy capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople. In the eyes of the Islamic conquerors, if they were able to take control of Constantinople, then they could easily topple the entire Byzantine Empire, and subsequently most of Europe. This conflict would lead to the First Arab Siege of Constantinople (674-678).1

After four years of bloodshed on the outskirts of Constantinople, the Byzantines were able to repel the Muslim army away from Anatolia by destroying their navy. Just two years after the Muslims’ defeat, the Islamic Empire underwent a civil war until 692. Between the years 695 and 717, the Byzantine Empire also fell into internal turmoil that led to eight emperors within twenty-two years. Under the leadership of the Umayyad caliphs, the Islamic Empire, seeing that the Byzantines were busy disputing among themselves, saw an opportunity to attack Constantinople again. Luckily for the Byzantines, they had a hunch that the Muslims would try to seize their beloved city, so they took the time to reinforce the city.2

By 717, Arab prince and general Maslamah ibn Abd al-Malik oversaw the Islamic Empire’s campaign to claim Constantinople and led his army straight for the capital. There, Maslamah tried to blockade the city with his navy, but this gave the prepared Byzantines an opportunity to unleash their secret weapon.3
The fire that was spout out from this hose started to incinerate the entire Arabs’ fleet. The Muslim soldiers started to throw buckets of water to subdue the flames but quickly realized that this was not regular fire. This was a special kind of fire that could not be put out with water. Seeing as how stopping the fire was futile, the soldiers quickly took off their cumbersome armor and leaped out into the water while the ones that stayed got lit on fire. Some unlucky soldiers who impulsively jumped overboard were still wearing their full set of armor and as a result, immediately drowned to the bottom of the sea. The fire that had been burning the ship started to spread out onto the water as if it was gasoline. These flames stretched out and the surrounding ships were also caught on fire. Some of the soldiers tried to swim away frantically, for the fire floated across the sea and burned those that were closest. From a distance, the surviving Muslim soldiers were witnessing their own comrades burning, screaming in agony from the top of their scorched lungs. No matter what they did, there was nothing that could be done to put out the flames that were covering their melting bodies. Even some of the spectating Byzantine soldiers shivered at the thought of being burnt alive while being completely surrounded by water. Once the Arabs realized that a significant portion of their ships had been engulfed in flames, they signaled a retreat. As the Arabs fled the scene to lick their wounds, the Byzantine soldiers cheered with victory.4
After Maslamah called off the blockade, the Muslims attempted to regroup outside Anatolia and wait for more of their men and supplies to arrive. Unfortunately for the Muslims, the Byzantines captured their reinforcements, so the Arabs had no choice but to travel back to Syria in defeat. With the help of Greek fire, the Byzantines were able to prevent the Islamic Empire from conquering Constantinople, as well as most of Europe. The Byzantines would continue to be the sole inhabitants of Constantinople until the Ottoman Empire finished them off in 1453.5
To understand the significance of Greek fire, it is important to have already mentioned the background to these Byzantine and Arab conflicts. But what exactly was this Greek Fire? How did it come about?

While the origin of Greek fire is not entirely known, it is widely believed that the creation of this destructive weapon came from a man named Callinicus, an architect who left Syria to seek refuge in Constantinople. After experimenting with several chemicals, he eventually created what is now known as Greek fire, a mixture that, when exposed to air, would spontaneously erupt into flames. Callinicus guarded the recipe extremely well, as only the Byzantine emperor and Callinicus’ family, the manufacturers, knew the exact ingredients used.6 It should be noted that during this time, the Byzantines saw themselves as Romans, prompting them to call this weapon ‘liquid fire’ or ‘marine fire.’ As for its physical appearance, it was said to have been a ‘wet dark liquid’ that most likely contained oil.7 According to twelfth-century Byzantine scholar Marcus Graecis, the ingredients used in Greek fire contained pure sulfur, salt, petroleum, Persian gum, pitch, pine resin, and dissolved nitre.8 As vague as it may seem, this is the closest we have to knowing the contents of Greek fire.
What made Greek fire so unique was its ability to burn on water, even when submerged. Obviously, this kind of fire could not be put out with water. Instead, some of the most common substances used that could put out Greek fire were sand and urine.9 This flammable weapon was shot out of a grand siphon, which was essentially a bent tube. This siphon would act as a propellant that would launch the fire outwards onto the target. Because of this, the fire was able to spray out at considerably far distances. This method proved to be successful and effective, as it brought devastation against its enemies and rarely backfired on its user.10

Apart from being sprayed out of a siphon, there were other methods to firing Greek fire, such as flinging them from catapults and throwing pots fueled with fire that acted as hand grenades that could explode on impact.11 The usage of Greek fire was not exclusive to sea warfare. It was also used on land, and the way it worked was similar to modern-day flamethrowers. The fire would be carried with handheld pumps, and to spray them, they used small flames at the nozzle to have the liquid set on fire. It worked just as effectively on land as it did at sea, with the exception of its small supply of the liquid.12
Greek fire was also shown to have a psychological impact on its victims. When it was used against Russian invaders in 941, the soldiers in full armor would rather drown at sea than be burned alive. Often times, the fumes that came out of the fire would cloud the area to the point where the sky darkened to night.13 The foreign invaders that witnessed this were shocked in fear. Russian survivors that made it back to their homeland told their kinsfolk that the Byzantines attacked them with “lightning from heaven.” The thought of being burnt alive with a seemingly invincible fire heavily traumatized both the Muslims and the Russians. Eventually, as gunpowder and cannons became more common in warfare, Greek fire became less of a surprise to future invaders like the Ottomans.14

As overpowered as Greek fire may have seen, it had its share of weaknesses. First of all, as mentioned earlier, while water was powerless to stop the fire, certain substances like sand and urine were able to put out the fire. Secondly, the fire was not effective during an open battle, since the enemies could easily dodge and move around the flames. Also, since production of the fire was kept secret, it was only used a handful of times. This was to lessen the chance of their enemies grabbing hold of the weapon and using it against them. The Byzantines wanted to make absolutely sure that they themselves would be the only manufacturers of Greek fire.15
Ultimately, because the process for making Greek fire was never written down and was kept extremely secretive, the weapon ceased to exist by the time the Ottoman Empire finally conquered Constantinople in 1453. Muslims did attempt to replicate Greek fire and did create their own version, but their fire was significantly weaker and for the most part only used on land.16 Despite the many attempts that people have tried to perfectly recreate Greek fire over the centuries, none have ever been successful. It is truly ironic how today, when we have nuclear weapons, lasers, drones, and high-tech weaponry all at our fingertips, we do not (and may never) have the knowledge and ability to precisely recreate the Byzantines’ best arsenal weapon: Greek fire.
- Global Events: Milestone Events Throughout History, 2014, s.v. “Leo III Defends Constantinople with Greek Fire.” ↵
- Global Events: Milestone Events Throughout History, 2014, s.v. “Leo III Defends Constantinople with Greek Fire.” ↵
- Global Events: Milestone Events Throughout History, 2014, s.v. “Leo III Defends Constantinople with Greek Fire.” ↵
- Global Events: Milestone Events Throughout History, 2014, s.v. “Leo III Defends Constantinople with Greek Fire.” ↵
- Global Events: Milestone Events Throughout History, 2014, s.v. “Leo III Defends Constantinople with Greek Fire.” ↵
- Science and Its Times, 2001, s.v. “Callinicus of Heliopolis,” by James J. Hoffmann. ↵
- World History Encyclopedia, 2011, s.v. “Greek Fire.” ↵
- Science and Its Times, 2001, s.v. “Marcus Graecis.” ↵
- Science and Its Times, 2001, s.v. “Callinicus of Heliopolis,” by James J. Hoffmann. ↵
- J. R. Partington, “A History of Greek Fire and Gunpowder,” Philosophy of Science 29, no.4 (October 1962): 436. ↵
- Norman Hepburn Baynes and H. St. L. B. Moss, Byzantium; an introduction to East Roman civilization (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1948), 306. ↵
- World History Encyclopedia, 2011, s.v. “Greek Fire.” ↵
- Robert Byron, The Byzantine Achievement : an historical perspective, A.D. 330-1453 (New York: Russell & Russel, 1964), 280. ↵
- Deno John Geanakoplos, Byzantium: church, society, and civilization seen through contemporary eyes (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1984), 114. ↵
- World History Encyclopedia, 2011, s.v. “Greek Fire.” ↵
- World History Encyclopedia, 2011, s.v. “Greek Fire.” ↵


62 comments
Emmanuel Diaz
The Greeks created something so powerful for their time and I understand why they never wrote it down as if it were to be known by all it would not be as practical nor have the element of surprise to enemies and then for be useless against others as there would be ways to stop it through tests and experiments. It must have been terrifying to be ready for a battle of swords and arrows only for it to quickly change and trying to survive against inextinguishable flames that traveled across the surface of water. the article was great!
Emmanuel Ewuzie
Greek fire sounds menacing. This secret weapon completely changed the tide of battles. This reminds me of the impact of firearms as firearms played a big part in European colonization. European firearms made it easy for conquistadors to conquer the Indians as they did have the firepower and weaponry to compete.
Kenneth Gilley
What an awful weapon! I suppose that Greek fire was the Byzantine equivalent to modern nuclear weaponry. Imagine being burned alive while surrounded by water. Imagine watching that happen to one’s comrades. It is no wonder that entire armies would have their morale destroyed by Greek fire. I wonder if we will ever discover the ingredients it was made from? This article was very informative and vividly written.
Michael Leary
Very interesting article about Greek fire, I have heard of it before and its use in naval warfare. I found it informative when it was talked about the effectiveness of the fire in water and how it did not have a tendency to backfire on the user. It seems like it was very useful for the Byzantines in their struggle to stay alive and protect Western Civilization from the Islamic invaders.
Jabnel Ibarra
Many modern inventions and weapons often turn out to be new iterations of technologies and weapons that already existed at some point in history. Greek fire, from what I’ve read about in this article, seems to be one such historical iteration of modern-day napalm. Its amazing to think that without the help of modern knowledge and technology the Byzantine empire was able to make a weapon so effective and powerful that we would be unable to recreate thousands of years later.
Alexander Manibusan
I absolutely loved the powerful ending of this article! While I’ve only heard of Greek fire I initially didn’t know much about it. I find it very interesting now, how the Byzantines had weapons similar to flamethrowers and grenades- things that seem to be only found in modern times. I’m very curious now on how this Callinicus used the ingredients mentioned to make such a horrific weapon.
Christopher Vasquez
Greek fire seemed deadly beyond comprehension; burning on and under water — that would cause psychological damage to nearly anyone who saw their comrades dying this way. It’s strange, as the author pointed out in this article, how humanity has been able to make so many technological developments, yet it can’t figure out the exact chemical composition of Greek Fire. If this fire could burn on water, I wonder how long would it take for the flames to extinguish themselves naturally. The family of Callinicus and the Byzantine emperor did a great job (perhaps too great a job) at keeping the secret of their deadly weapon. I also was not aware that the Byzantines fought Russian invaders with this weapon, or that they thought it was “lightning from heaven.”
Jose Sanchez
This was a very well written article. Reading about Greek fire always amazes me. It seems like such an advanced weapon to have at one’s disposal, and yet the Byzantines had it. And as you mention, we cannot replicate it today. I would say the closest thing we have to it would be napalm. I commend the Byzantines for their secrecy.
Jonathan Perez
I found this article very interesting. Often times when we discuss military history it is about generals or key battles but in this case the focus was more on the weapon not only in its physical effectiveness but in its psychological effectiveness as well. The author does an excellent job of using imagery to describe the horrors of those who faced the Greek Fire while also doing a great job at describing why it was so effective. Overall the author did an excellent job of explaining and made the article an enjoyable read.
Saira Castellanos
I had never heard of Greek Fire, and its pretty cool. Reading this made me think about the fire weapons we used i believe in World War I, but we stopped using them because it was too destructive, and people were dying a slow and painful death. The invasion of Constantinople clearly shows how much destruction the fire causes and such horrible things. Overall, great article! it was a really good read.