Communication among humans is essential, and as we evolved, we have come to master the art of speaking. Through time and research, linguists have come to the conclusion that, because many languages from Europe and Asia share multiple similarities in vocabulary, there must have been a language from which these languages originally derived. The fact that a single language can develop into two or more different languages is due to language change.1 This language change through Europe and Asia refers to the Indo-European languages. These Indo-European languages are believed to have derived from an ancestral language known as Proto-Indo-European, which is no longer spoken.2 Because these native speakers left no evidence of writing, linguists have yet to solve when this language branched out to the various Indo-European languages we know today.

There are ten major branches to the Indo-European family of languages: Tocharian, Indo-Iranian, Hellenic, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Albanian, Celtic, Italic, Germanic, and Anatolian. These branches also branch to other major languages, such as Russian, Polish, Spanish, German, English and many more. Words derived from the Indo-European languages are similar among each other, most commonly found in numerals from one to ten, body parts, plants, and animals.3 These findings have opened the gates for numerous researchers, including the famous philologists Sir William Jones and Franz Bopp.

Sir William Jones was an English philologist who first introduced the theory that all these languages were derived from the same language. Jones knew twenty-eight languages, which set the groundwork for his future findings. In 1786, he published The Sanskrit Language, in which he suggested that Sanskrit, Greek, and Latin shared a common root and were also related to other languages.4In 1788, he delivered a famous speech, which is considered the beginning of Indo-European language studies and comparative linguistics. Jones writes:
“The Sanskrit language, whatever be its antiquity, is of a wonderful structure; more perfect than the Greek, more copious than the Latin, and more exquisitely refined than either, yet bearing to both of them a stronger affinity, both in the roots of verbs and the forms of grammar, than could possibly have been produced by accident; so strong indeed, that no philologer could examine them all three, without believing them to have sprung from some common source, which, perhaps, no longer exists.”5
After Jones’ death, different scholars continued to investigate his findings. Franz Bopp, a German linguist, discovered the importance Sanskrit had in comparative studies of the Indo-European languages and analysed grammatical structures and compared their morphology.6 His work concentrated on tracing the origins of five different languages by focusing on their verbs. Then in 1820, he extended his studies to include grammar. Bopp’s findings resulted in the science of comparative grammar that we study today.
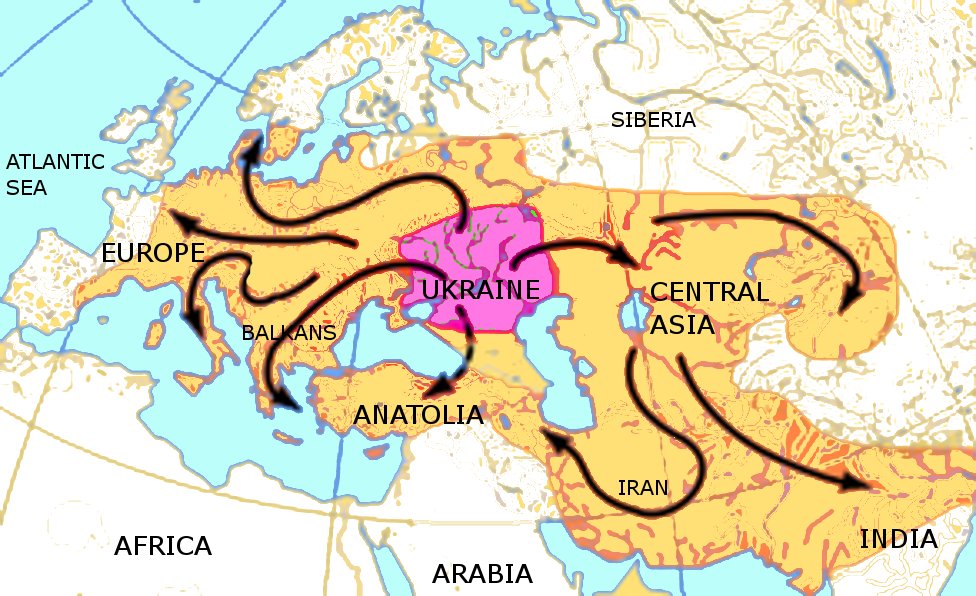
Although there is no literary evidence for what happened to the Proto-Indo-European native ancestors, it has been hypothesized that they migrated to different locations. As time passed, the language evolved greatly in a way that new languages began emerging, causing the original to perish. Despite the current exploration, researchers are still puzzled about the original Indo-European language, and they continue to search for answers today.

- Benjamin W. Fortson, IV, Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction (John Wiley & Sons, 2011), 4. ↵
- Fortson, Indo-European Language and Culture, 11. ↵
- Fortson, Indo-European Language and Culture, 41, 52, 67. ↵
- Encyclopedia of World Biography, December 2006, s.v. “William Jones Biography.” ↵
- Fortson, Indo-European Language and Culture, 9 ↵
- Franz Bopp, Analytical Comparison of the Sanskrit, Greek, Latin and Teutonic Languages, Shewing the Original Identity of Their Grammatical Structure (1820) (Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing, 1974), VIII). ↵


31 comments
Alexis Soto
This was a great read and cool topic! It is interesting to think that many of the modern languages of today derived from a single common language. It was interesting to read of who first proposed the idea of a common ancestral language and what evidence is used to help prove the theory correct. Reading about this shows me how similar and connected we as humans truly are.
Teresa Valdez
I did not think it was possible to know 28 languages. Although, knowing that these languages had similar origins, it makes sense that each of the languages came easily to Jones. If only I could learn languages like that! The article defends Jones’ theory well, expressing that both grammar and vocabulary point to a ancestral Indo-European language. Strong evidence served the article well. Wonderful work!
Yesenia Cardenas
It fascinating how languages that are so different today have a common ancestor. It makes sense how there are common words amongst different languages. I was wondering why Portuguese is not in the Romance section of the image.
Mariana Sandoval
I always find it fascinating how there are so many languages and how they evolved. I took a comparative anatomy class where we studied the anatomy of different animals and how we were all connect, how we came from a common ancestor, etc. You can do the same thing with languages and trace the evolution of the language to a common ancestor. It’s really interesting and shows a lot about our history.
Jezel Luna
I did not realize how many major branches the Indo-European family languages had, as well the ones that branched off the major ones. This is a complex subject, but you did a great job describing and illustrating the Indo-European Language.
Rachel White
Not only was your article very informative, but the images that you utilized in the text helped the reader to fully understand the idea you were conveying. Images are a large part of understanding text and your article did an amazing job of proving this. Although I was familiar with the Indo-European Language being around and evolving, I had no idea how many languages it evolved into before it reached the languages that we are familiar with today. Great topic and illustrations!
Celina Resendez
I was really interested in reading your article when I saw the title because I recently took a class that looked at the history of the English language. We went into depth about how the language started and the many, many changes it has gone through. I enjoyed your article because it took what I have learned even further. If you have room for an elective class or an extra english course, you should look into History of the English Language with Dr.Hill. It’s a really fun and interesting class!
Diana Moreno-Gutierrez
The world continues to evolve and although we may not see it, everyday things such as languages evolve too. It makes sense that the language we have today is based off of previously spoken languages but I never really looked into it. Even our language has a history of its own. Very informative article, great job!
Smithe290
Thanks for the post.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on dabbbeagagdbbgek
Analina Devora
I really enjoyed this article and how well the pictures illustrated your information. It’s bizarre how language evolves and changes over time and how there’s evidence of it’s origins still today. People may not even think twice about how the words coming out of their mouths came to be.