

It’s 1346, and a killer is stalking European cities. Soon, bodies will be dropping dead, towns will be wiped out, infected rats will be taking over cities, and worldwide panic and insanity will settle in. Through much of its history, the Afro-Eurasian world had been struck with fatal pandemics before. Some epidemics would affect certain parts of the world, others would engulf the world in their deadly desires. The Bubonic Plague, also known as the Black Death, is arguably the most fatal pandemic the Eurasian world has ever witnessed. The people of Europe were not prepared to combat such a deadly disease, and would not be able to fight adequately against its unknown powers.
The Black Death spread through Europe like wildfire. It started during the winter of 1346, when a Mongolian army prepared to capture the town of Kaffa, located between the borders of Europe and Asia right on the edge of the Black Sea. Kaffa was known as one of Europe’s greatest trading centers, which would become an important catch for the Mongolian empire if captured. The Mongol army was infected by the Black Death, and they began rapidly dying on their expedition to the city of Kaffa. Thousands of Tartar Mongolians were dying daily, rapidly decreasing the Mongolian leader’s options on how they would capture the city of Kaffa. Regardless of any medical attention, once the disease was visible to its victim, it was an automatic death sentence. Though the Mongol leader had lost his troops to the Black Death, he was not going to waste the time or his troops on an attempt to storm the city. Instead, the Mongol leader took their giant catapults and launched their infected corpses over the walls and into the city of Kaffa. Once the corpses were in the town, people in the town of Kaffa started to die, and those that were still alive were desperate to survive this new sickness, and they began fleeing the town. People boarded ships and sailed southward into the Black Sea.1 Unfortunately, it was too late; their bodies had already been infected with the disease—and thus the spread of the Black Death in Europe began.
Those who fled Kaffa first brought the disease to Constantinople, and by 1347, the disease had reached the level of an epidemic. Constantinople was a prime trading hub for people all over Europe and Asia. Traders would come to Constantinople to sell their goods in the Byzantine city. Therefore, once the traders were done selling their goods and were ready to leave, their ships had already been infected by the disease that had hit Constantinople. But the traders left the city on their ships, unknowingly infected and carrying the disease even further into Europe. The ships leaving Constantinople contributed to the spread of the Black Death southward into the lands of the Mediterranean. The Black Death hit the port cities in Palestine, in Egypt, in Greece, in Italy, and also in North Africa.2

This Black Death was a disease unlike any other, one that was so unknown, that nobody knew how to handle it. Europeans were ill-prepared to combat what this disease would do to its victims. The Black Death spread through contact, much like most diseases. When it came to exposure to this bacteria—Yersinia pestis—it’s said that the easiest way for this disease to spread was through the skin. An open wound, a bug bite, a scratch, cracks in the skin was all it took for this bacteria to enter the body. It was carried by different parasites such as lice, fleas, ants, and other bugs, much of these found on rats and other vermin. The bacteria could be transmitted either from the parasite bite itself or even from the scratching of a bite, leaving an open wound for transmission. Once someone had become exposed, they would enter the incubation period. The average incubation period ranged from three to five days. Although that was the average, there were also cases where signs of the disease would show after 36 hours, while others wouldn’t show symptoms until fourteen days after exposure. This made it difficult to find a true minimum and maximum number of days for the incubation period.3 The symptoms of this virus were painful and deadly. After roughly three days after being exposed, a smooth yet painful lymph gland swelling known as a bubo would start to appear. These buboes were typically found in the groin area, armpits, and neck. In some cases, victims of the Black Death could potentially feel pain in those areas even before the bubo had become visible. Other symptoms included but were not limited to high fevers, muscle aches, vomiting, seizures, prostration (or weakness), chills, and headaches. Needless to say, it was a very excruciating way to die.4 The Black Death not only had effects on one’s body, but also affected Europeans socially. Since it was such a fatal disease, mass hysteria kicked in and everyone was living in terror. People began to disregard the rules because they saw no point in following them anymore if they were going to die. Brothers began abandoning their brothers, parents started to neglect their children, and everyone was made to fend for their own.5
Now that the Plague stalking Europe had spread through its ports, it began to spread even more. By 1348, the plague reached the French city of Avignon. At the time, the city of Avignon was the headquarters of the Catholic Church and of Pope Clement VI. The plague hitting the French city of Avignon would start to affect religious affiliations. Because of how deadly this plague proved to be, priests began fleeing their town in the hope of escaping this killer. Unfortunately, this caused people to start questioning priests and their loyalty to their religious work. It was then that even religion began getting affected by the Black Plague.6 This plague truly put some religions to the test.

Europeans were looking for someone to blame, and unfortunately, their fingers pointed to the Jews. Jews were accused of poisoning wells, foods, and streams. Because everyone was living in hysteria, many people believed that Jews were to blame for the deaths, and they began torturing Jews to death, often by burning them to death.7 People felt that Jews should suffer and die in a way that would be painful, yet also cleansing of the plague, which explains why burning became a way of torture. Not only did the Black Plague affect the Jews, but it also began to affect Christians, who would start forming ideas for why this plague began in the first place. Many believed that the plague was the righteous judgment of God because of how sinful humanity was. While it was very seldom, there were still people that had hope that through prayers and processions, God’s vengeance of the plague could be resolved. The plague also began causing problems for the Church. There were fewer and fewer priests who were able and willing to hold parish services, so this made it difficult to keep the religious services running.8
Many cities that had become infected with the plague were living with the dead piling up. The corpses of those who lost their lives to the plague were lying around creating piles of the dead, practically taking over the city. The problem with this was that the corpses needed to be removed and buried, but because of how infectious this plague seemed to be, nobody wanted to do the tasks of touching any of the corpses. This meant that this dirty work was mainly reserved for low-class thugs and criminals. Not only were societies struggling to figure out who was going to bury the bodies, but they also struggled with where the bodies were going to be buried. European Christians expected to be properly buried, preferably on the sacred ground by a church. But because of how many people were dying and how fast they were dying, burial options became slim to none. The Renaissance writer Giovanni Boccaccio wrote,
“There was not enough concentrated (sacred) ground to bury the great multitude of corpses arriving at every church every day and almost every hour… So, when all the graves were occupied, very deep pits were dug in the churchyard, into which the new arrivals were put in the hundred. As they were stowed there, one on top of another, like merchandise in the hold of a ship, each layer was covered with a little earth, until the pit was full.”9
Due to the lack of space for graves and the belief that fire would cleanse infection, some communities turned to cremation of the bodies, which wasn’t a typical way of burial at the time. Needless to say, the Black Death affected people physically, mentally, and spiritually.
France had been completely overrun by the Black Death, and it wound up reaching the banks of the English Channel. There was hope that the infection would stop there, due to the massive waterway separating England from the continent. Unfortunately, this was not the case. As mentioned before, not only could people spread the disease, but rats and other vermin could too. So, from one rat-infested town to another, the rats made their way onto trading vessels headed to the lands of England, Germany, Poland, and Russia, which wound up devasting Moscow by 1352. This stalker of death was on a killing rampage that seemed impossible to stop, no matter what attempts were being made.10
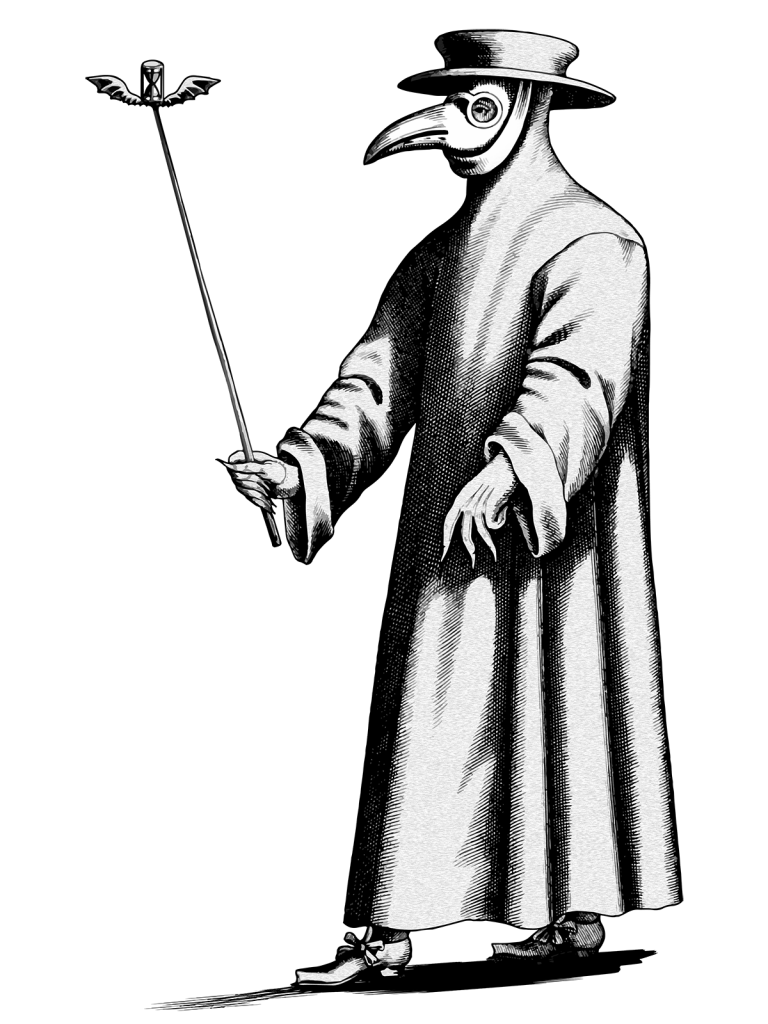

How did Europeans attempt to stop the plague from spreading? Many of us have seen the sinister costume that was worn during this time, but don’t know the reasonings behind it. The costume would be known as Doctor of the Plague. It consisted of a beaked white mask, a black hat, and a waxed gown.11 A royal physician, Charles de L’Orme, described the costumes as such:
“The nose is half a foot long, shaped like a beak, filled with perfume with only two holes, one on each side near the nostrils, but that can suffice to breathe and carry along with the air breathes the impression of the herbs enclosed further along in the beak. Under the waxed coat, we wear boots made in Moroccan leather from the front of the breech’s smooth skin, the bottom of which is tucked into the breeches. The hat and gloves are also made of the same skin…with spectacles over the eyes.”12
At the time, it was thought that different herbs and perfumes could cleanse and/or purify the air, which is why the beak of the mask was filled with up to sixty ingredients. Some of these ingredients included honey, cinnamon, agarics, ground mummia, opium, and desiccated viper. The goggles were used to help apply leeches to the buboes to try to suck out the infection. Finally, the wooden cane was used to help remove patients’ clothes, record their pulse, and keep themselves at a safe distance.13 Regardless of doctors’ best efforts, essentially nothing stopped people from dying of this disease, and many of the doctors fled during the plague hoping to save themselves.14 Through a lot of trial and error, even with most doctors’ best interests at heart, very few would find a way to combat the disease. One of the most famous doctors in Italy at the time, Gentile da Foligno, wrote about what he thought was a defense against the Black Plague. For one, people should be very aware of what they are consuming in terms of food. Fish should be avoided, as well as lettuce if it had been left out in the cold. It seemed imperative to eat good meat such as chicken, gelded cows, and lactating goats. Second, people should take prescription medicine that would help purge and cleanse the body. Third, roughly two or three times a week, people were recommended to indulge in theriac—a paste made as an antidote to poison. Finally, it was highly stressed that people create large fires within their homes in an attempt to keep the infected vermin away.15 Many doctors would do all that they could to try and put the Black Death to an end.
Regardless of everyone’s best efforts to stop that plague, it would not end with a happy ending. The Black Death wound up killing between 100-200 million people, which was roughly 60% of the population of Europe at the time.16 While the first wave of the plague would come to an end in 1351, the nightmare of the second plague returned in 1361 and would, unfortunately, bring a cycle of terror to Europe once again.17
Throughout this writing process, there are many individuals to whom I’ve come to owe the utmost respect and gratitude. First, I would like to thank Jose Chaman for his guidance in helping me choose my topic and prepare my project proposal. Second, I would like to thank my colleagues at The Learning Center, who continuously encouraged me while writing my article. Third, I owe the utmost gratitude to Dr. Whitener for giving me this opportunity to display my work publicly and for providing me with much-needed revisions that have helped strengthen my writing skills. Finally, I’d like to thank my parents for providing me with a great support system and the confidence I needed to complete my writing.
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 17. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 18-19. ↵
- James Cantlie, “The Signs and Symptoms of Bubonic, Pneumonic, and Septicæmic Plague,” Br Med J 2, no. 2078 (October 27, 1900): 1229–32. ↵
- Stephanie Eckenrode, “Bubonic Plague,” Salem Press Encyclopedia of Health, 2021. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 71-72. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016) 25-26. ↵
- S. K. Cohn, “The Black Death and the Burning of Jews,” Past & Present 196, no. 1 (August 1, 2007): 4. ↵
- John Aberth, The Black Death: The Great Mortality of 1348-1350, Second, The Bedford Series in History and Culture (Bedford Books, 2005), 79. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 22. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 24. ↵
- Christian J. Mussap, “The Plague Doctor of Venice,” Internal Medicine Journal 49, no. 5 (2019), 1. ↵
- Christian J. Mussap, “The Plague Doctor of Venice,” Internal Medicine Journal 49, no. 5 (2019), 2-3. ↵
- Christian J. Mussap, “The Plague Doctor of Venice,” Internal Medicine Journal 49, no. 5 (2019), 3. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 33. ↵
- John Aberth, The Black Death: The Great Mortality of 1348-1350, Second, The Bedford Series in History and Culture (Bedford Books, 2005), 49-51. ↵
- Christian J. Mussap, “The Plague Doctor of Venice,” Internal Medicine Journal 49, no. 5 (2019), 2. ↵
- Emily Mahoney, The Black Death: Bubonic Plague Attacks Europe (New York, NY : Greenhaven Publishing LLC, 2016), 86-87. ↵




62 comments
Michaell Alonzo
Hey Emily, congrats on your article’s recognition/ award. This post was so beautifully written and fascinating to read. This page has an astonishing quantity of specific information. I have read about the bubonic plague before but it’s always interesting to read about it and now see how Covid 19 fits into the pattern of past plague outbreaks. I really loved the visuals you used because they truly fitted into the tale you were telling. You not only portrayed the physical affects the epidemic had on the individuals afflicted by it, but also the social and religious effects of it, which showed just how completely afraid these people were.
Fatima Esparza
This article on the Black Death is very informative! Before, I knew that it affected the health of large populations throughout Europe and other countries in the eastern hemisphere, but not religion. It is interesting that this plague affected the way some people thought about religion, and many of them were put to the test during this time. Catholic priests fleeing portray their beliefs in their faith. I would see why many questioned these acts during this time.
Luke Rodriguez
This was a fascinating article from the very beginning; it hooked me. The Black Death was one of the deadliest diseases ever to exist, but how it affected the people were fascinating. With the disease spreading across Europe, it was disturbing to see how families and communities turned on each other looking for someone to blame. It could be looked at how people had reacted to Covid when that had first happened.
Elliot Avigael
Congratulations, fellow awardee! Your title immediately grabbed my attention, and I also appreciated your narrative structure. I’ve been looking for a well written article on the Black Death and this one took the prize. I think the impact the Mongols had on the world is incredibly underrated, at least in regards to the Black Death. I especially liked how you added the addition of ethnic scapegoats (in this case the Jews), which seems to be a trend when it comes to pandemics.
Laurel Cox
I found the article to be incredibly well written and thorough in its content. I found it very interesting that the plague not only affected the population and health system of Europe, but the social and religious aspects as well. I didn’t realize that many people saw the plague as a sort of condemnation for the sins of humanity, it’s always interesting to see how people or societies react in dire situations such as these. Also, I never knew that the plague originated from Mongolia, and it seems interesting that their first thought for getting over the plague was to rid the bodies, which was partly correct.
Isabella Lopez
I’m so impressed! This was such a well thought through article. You described years worth of information so genuinely and with great context. Typically when you hear about the Black Death it sounds so curse like, almost something from a fantasy, but you brought it back to reality with precise detail on its symptoms and how it socially, religiously and physically effects people.
Side note: Congratulations on your award. It was much deserved!
Priscilla Leal
what an informative and engaging article. a disease does not discriminate no matter what time period we are on. the black plague is very similar to covid 19 in the case where they both experienced mass hysteria, incubation/quarantine rules, the low class people having to work through the epidemic etc. what really surprised me was the introduction, and how the mongolians spread the disease by catapulting infected corpses.
Victoria Castillo
First of all, I love how you described the Black Death as a serial killer in your title as is it really depicts the ominous terror the people must’ve felt when introduced to an unseen threat. Secondly, the way you not only described the physical effects the plague had on the people affected by it, but also the social and religious effects of it showed just how purely terrified these people were that they resorted to blaming an entire ethnoreligious group for its creation. It was also very interesting to see how the plague was even harnessed as a use of power as you described how the Mongols used the plague as an advantage. All in all this was a really great article!
Clarissa Liscano
I found this article to be really fascinating and was captivated the entire time I was reading it. Congratulations on your nominations; they are well-deserved! I won’t lie; when reading, I did notice very few similarities between the covid-19 virus and the bubonic plague. Just in terms of how quickly it spread and how many people it killed. I was particularly shocked to learn that the disease was blamed to Christians and Jews. In general, fascinating article.
Danielle Sanchez
The article was well detailed and insightful! This article pinpoints the origin of the black death. What I found most interesting was how the Mongol leader lost his army to the plague and catapulted the bodies of the deceased into the city of Kaffa. Also, how the Europeans tried to stop the spread with a mask that had a beak at the end which contained sixty ingredients. Overall, well done and this was something I enjoyed reading!