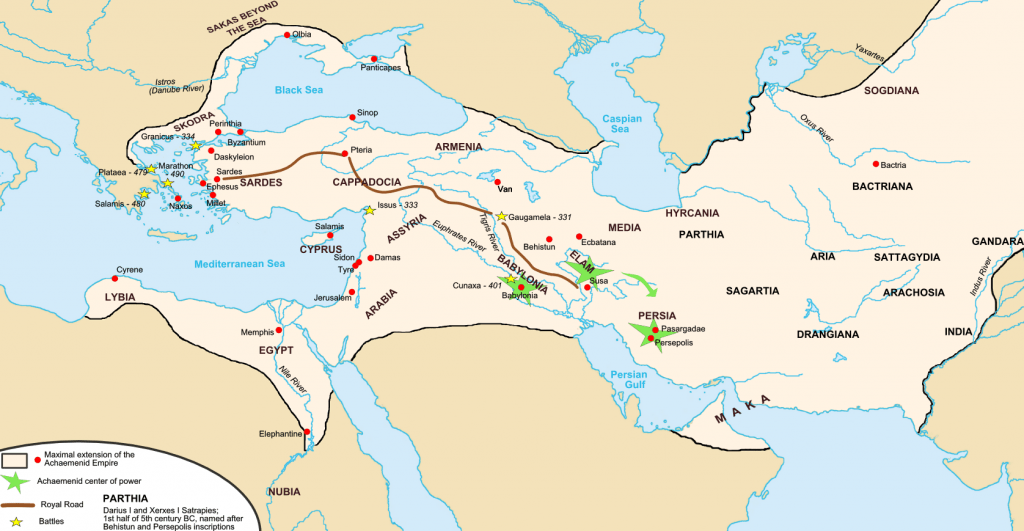
In the fifth century BCE, communication between the rulers of the Persian Empire and the regions they governed was very important. People needed to know the laws of their king and how to live under those laws. Merchants and farmers needed to know how much they were getting taxed on their goods. These farmers needed to come up with a price so they could afford to live and pay the empire’s demands. Darius I, who was the third Persian emperor of the Achaemenid dynasty, came up with the idea of a road that would link the vast territory of the Persian realm. This road was called the Persian Royal Road.1

The road was built from Susa all the way to Sardis, which stretched 1677 miles. The trip from Susa to Sardis would take about two months to complete by foot, but with a healthy and fast horse, a traveler could go from one end to the other in seven to nine days. To go from the capital of Susa directly to Sardis one would travel over the Tigris River, Euphrates River, and the Halys River. During the journey, travelers would pass by the cities of Karim, Jarmy, Nineveh, and some passed through Assyria if they wanted, which would not greatly detour travelers from the original route.2 The road would also branch off or lead to Syria and Armenia if travelers needed to go that way.
The Royal Road was developed with the purpose of allowing travelers to travel swiftly from one city to another, and for information to be passed through all the cities of Persia. Along the road, checkpoints were set up to ensure safety and for travelers to have rest stops where they could rent fresh horses, or acquire supplies they might need. These stops were set up along every river crossing and at every entrance to each city. The stops were also built because of long stretches of desert or barren land. In order to ensure safety, the Persian guards would have certain areas on the road to patrol, guaranteeing that every traveler passed through the checkpoints safely and were not causing problems in the cities.3 To compare this to modern day, this would be like highway patrol and border patrol when entering and leaving a country. Since the main reason for Darius to install this Royal Road was for faster communication, he set postmen or, as the people of that time called them, pirradazis, at the checkpoints. These men were given the fast horses to deliver messages all along the road. Some even traveled to surrounding kingdoms to deliver messages. Many of these pirradazis were set up at each checkpoint so the communication could travel faster; and for those living in the cities, they could also send messages to and from their city through these men. These couriers would travel in any weather and at any time of day.4
From the development of the Persian Royal Road, many inventions, groups, corporations, and jobs were established that otherwise may not have been created or thought of. From this road, a postal service was created that was later used by many empires as a type of communication throughout their own empire. Although Darius created this road to help his empire thrive and expand, this road would be more appreciated and admired than he could ever think of.
- Jerry Bentley, Herbert Ziegler, and Heather Streets Salter, Traditions & Encounters: A Brief Global History Volume 1, 4 edition (McGraw-Hill Education, 2015), 88-89. ↵
- W. M. Ramsay, The Historical Geography of Asia Minor (Cambridge University Press, 2010), 27-34. ↵
- Maria Brosius, The Persians (Routledge, 2006), 20-25. ↵
- Vernon L. Provencal, Sophist Kings: Persians as Other in Herodotus (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2015), 158-166. ↵


26 comments
Matthew Swaykus
We learned about this in class recently! The author did a good job pointing out not only the necessity of the road, but the extreme usefulness as well. This road was a wonder to the world. The time of travel was reduced from months of perilous journey to possibly a little over a week. Roads were dangerous and many things could happen to merchants and transported goods. The roads not only created efficiency but may have very well saved lives.
Christopher Hohman
Nice article. We have just covered the Persian Empire in my class. The Persians sure were something else. They were just nomads , but they became so much more than that. They really were something. The royal roads were a huge accomplishment that linked the parts of the empire together at a time when people did not move very quickly. The Persians also developed underground canals called quanants which stored water away from the sun.
Andrew Dominguez
Before this article Ive never heard of the Royal road. It takes sense that roads were needed in order to speed trade up in the country. With this increase in roads trade would increase since it wouldn’t be as difficult to send items. Im surprised they had checkpoints to check on their citizens safety. Usually when i think of check points it usually not for the safety of the citizens.
Angela Rodriguez
Such an informative article. I had heard about the Persian Royal Road before but never knew there were various check points set up along the way. I believe that y Darius creating this road he was such an intelligent being, he knew that through this development, transportation would be faster and easier, possible growth in the surrounding cities and also allows for effective communication. It’s great to know that this road had such an impact from Susa all the way to Sardis.
Tyler Sleeter
Great article with lots of information. I had heard of the Persian Royal Road and its importance for communication throughout the Persian Empire. I did not realize how much the road was like modern day systems of travel around the globe. From this road they had mail delivery, messages of state delivery, protection, and even checkpoints. It is fascinating to me that all this came out of a desire to move messages throughout the empire in a faster, more efficient way. To reduce travel time from several months to less then ten days is quite an accomplishment.
Tara Sellers
This article tells us why the Royal Road was built. It makes since with such a big empire that they would need roads. You need a way to transport goods, troops, and information. However, I did not realize they put checkpoints in to help ensure safety of people traveling down the road. It is impressive that even back then they are proactive about protecting their people and goods.
Clarissa Bustamante
I’ve never heard of Persian Royal roads before, but I have heard of Silk roads. It’s interesting to read that people would come up with ideas of connecting roads and highways. And with doing that they used it to transport goods and trading a lot easier. It was very smart to build the road because it was mostly likely one of the reasons why their society developed and expanded so well and fast.
Mario Sosa
To be honest, I do not know much about the Persians so this article helped me understand how they were able to communicate with different cities. It is intriguing how even back then they used checkpoints at are similar to modern day border patrols or highway patrols. I am now curious about what else Darius achieved during his time as emperor. Nice work on the article!
Sam Vandenbrink
Its hard to believe they had roads so long ago even before cars, from what they sounds like they seem more like walking paths, great article very informative! Didn’t know anything about the Persian royal roads so it was allot to learn in a little article, but I feel like I now have a very strong understanding of what the Persian roads were and how they were used!
Hayden Hollinger
This was a topic I had no prior experience of so I was pleasantly surprised to learn of these rail roads. I thought this was a well written article that was pretty short but still managed to get its point and the main facts across. I was very impressed with the length of the rail road and was impressed to read that the time to travel the distance was cut down so substantially with the use of a healthy horse.